Dec 4, 2025
What is Natural Language Understanding (NLU)?
Understanding human language is deceptively hard for machines. Words are full of nuance, context, and hidden intent, and without the right tools, even the smartest systems stumble.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) bridges that gap by interpreting meaning, detecting intent, and enabling technology to respond in ways that actually make sense to humans.
From chatbots to voice assistants, NLU is what turns raw language into actionable insights, improving interactions, automating workflows, and driving smarter decision-making.
In this post, we break down how NLU works, where it’s applied, and why it’s no longer optional for businesses that want intelligent human-computer communication.
At a glance:
NLU enables machines to comprehend human language by interpreting meaning, context, and intent, going beyond basic NLP tasks like tokenization and syntax analysis.
NLU powers smarter interactions. It drives chatbots, voice assistants, and AI tools that understand user intent, detect sentiment, automate tasks, and deliver personalized responses.
Implementation requires robust capabilities. Multilingual support, continuous learning, rapid data processing, system integration, and action mapping ensure accurate understanding and real-time execution of tasks.
Challenges include ambiguity, slang, evolving vocabulary, sentiment detection, system integration, and data privacy, but domain-specific models and ongoing training can overcome these hurdles.
CubeRoot utilizes NLU to transform engagement. Its Voice AI platform delivers human-like, multilingual conversations, automates lead qualification, debt collection, policy renewals, support, and feedback, enabling faster, smarter, and more personalized customer experiences.
What Is Natural Language Understanding (NLU)?
NLU is a branch of artificial intelligence that helps machines truly understand human language. Unlike basic keyword matching, it interprets the meaning, context, and intent behind words.
NLU goes beyond the surface of a sentence. It analyzes grammar, sentence structure, and semantics to figure out what a user actually wants.
In practical terms, NLU allows computers to:
Understand user intent—distinguishing subtle differences between phrases like “Book a flight to Delhi” and “Can you tell me about flights to Delhi?”
Detect emotions or sentiment in text or speech
Respond appropriately in conversational or task-oriented interactions
For example, it can distinguish between “Book a flight to Delhi” and “Can you tell me about flights to Delhi?”, even though both mention the word “flight.”
By capturing context, intent, and nuance, NLU enables machines to comprehend human language in a precise and context-aware way. This capability powers smarter chatbots, voice assistants, and AI tools that can interact naturally with users.
How Natural Language Understanding (NLU) Works
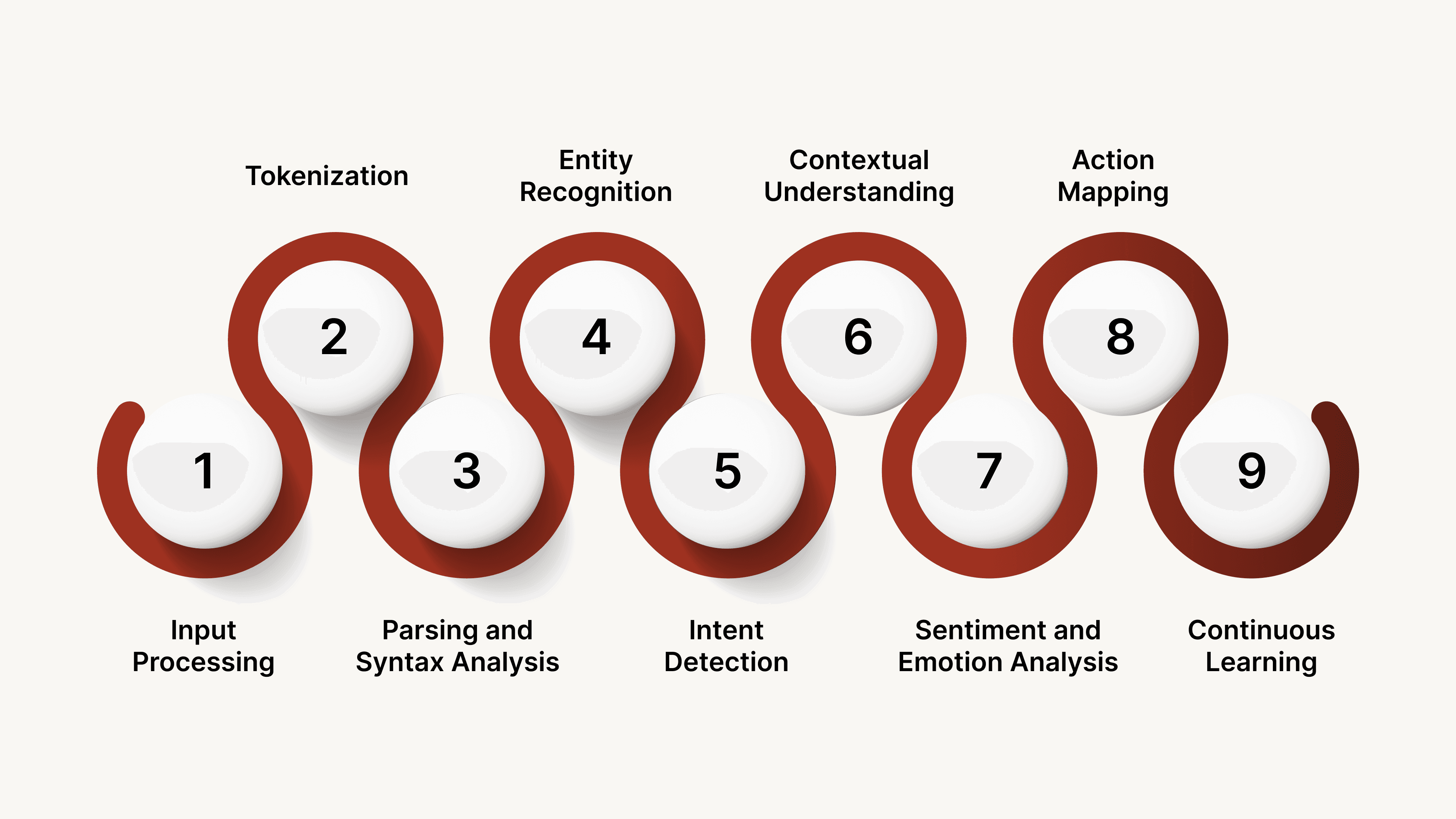
NLU processes human language in a series of steps, transforming unstructured text or speech into structured insights that machines can understand and act upon.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step look at how NLU works:
Step 1: Input Processing
The system first receives raw input, which can be typed text, chat messages, or voice converted into text. During this step, the input is cleaned and preprocessed. Punctuation is standardized, spelling errors are corrected, and unnecessary symbols or stopwords may be removed. This ensures the system can focus on the meaningful content of the message.
Step 2: Tokenization
The cleaned input is broken down into smaller units called tokens, which are individual words, phrases, or symbols. Tokenization allows the system to analyze the sentence at a granular level, understanding how each part contributes to the overall meaning.
Example: In a customer query, “I need to check my account balance before paying my credit card,” the tokens would be “I,” “need,” “check,” “account,” “balance,” “paying,” “credit card.”
Step 3: Parsing and Syntax Analysis
The system examines grammar, sentence structure, and relationships between words. Parsing helps the machine identify subjects, verbs, objects, and modifiers, providing a foundational understanding of the sentence. This step is crucial for distinguishing similar sentences with different meanings.
Step 4: Entity Recognition
Using Named Entity Recognition (NER), NLU identifies important details such as account numbers, payment dates, product names, or transaction IDs. These entities are essential for executing tasks accurately.
Step 5: Intent Detection
NLU identifies the user’s intention, which is the action they want to perform. Machine learning models classify the query into predefined intents such as checking an account balance, tracking an order, or scheduling an appointment. Accurate intent detection ensures the system responds correctly.
Step 6: Contextual Understanding
The system uses context from prior interactions to maintain meaningful, coherent conversations. This helps resolve ambiguity and ensures the system interprets follow-up questions correctly.
Example: If a user first says, “I want to pay my credit card,” and then asks, “Can you do it for the full amount?” the system understands that “it” refers to the credit card payment.
Step 7: Sentiment and Emotion Analysis
NLU evaluates the tone, sentiment, and emotions expressed in the input. Recognizing whether a user is frustrated, happy, or confused allows the system to respond more empathetically and appropriately.
Example: Detecting frustration in “My order hasn’t arrived yet” may prompt the system to prioritize the query or escalate it for faster resolution.
Step 8: Action Mapping
After understanding intent and entities, the system maps them to specific actions or responses. This could be executing a task such as processing a payment, sending an order update, or generating a conversational reply. Action mapping ensures that the conversation is actionable, not just understood.
Step 9: Feedback and Continuous Learning
Advanced NLU systems learn from each interaction, improving over time using supervised or unsupervised learning. They adapt to new phrases, slang, regional variations, and evolving contexts, which enhances accuracy and makes conversations more natural.
Example: In a query like “Schedule my doctor’s appointment for next Tuesday,” the entities are doctor and next Tuesday, allowing the system to confirm availability and book the appointment efficiently.
Also read: Conversational AI for Customer Service: Benefits and How It Works
NLU vs NLP vs NLG: Understanding the Differences
Artificial intelligence interacts with human language in multiple ways, but NLU, NLP, and NLG serve distinct purposes. Knowing the differences helps businesses choose the right approach for chatbots, voice assistants, and AI-driven communication tools.
NLU | NLP | NLG | |
Purpose | Helps machines comprehend meaning, intent, and context | Enables machines to process and analyze human language | Generates human-like text or speech from data |
Focus | Semantics, intent, sentiment, context | Syntax, grammar, keywords, entity extraction | Content creation, automated responses, summaries |
Example | Understanding that “I can’t log in” is a login issue, not a password reset | Identifying keywords like “login,” “account,” or “password” in a customer message | Crafting a reply like “I can help you reset your login. Here’s how…” |
In practice, these technologies often work together: NLP structures the input, NLU interprets it, and NLG crafts a response.
For instance, a customer asks, “Can I get a refund for my order?”—NLP identifies the key entities, NLU understands the intent (refund request), and NLG generates a natural response like, “Sure! I can help you process your refund. Here’s what you need to do next.”
By combining these layers, AI systems can move from rigid command-based interactions to fluid, human-like conversations that improve customer satisfaction, reduce support workload, and drive engagement.
Applications of Natural Language Understanding
Understanding customer intent at scale is a major challenge. NLU solves this by interpreting context, sentiment, and meaning, letting machines respond appropriately and consistently. The result is faster service, fewer errors, and more personalized engagement.
1. AI-Powered Customer Support
NLU enables chatbots and voice assistants to understand customer queries accurately, even when phrased in natural, conversational language. Instead of relying on keyword matching, these systems can detect intent and context to route issues or provide solutions instantly.
Example: In BFSI, a customer asking, “Why was my credit card payment declined?” can be understood as a payment inquiry. NLU helps the system distinguish it from account balance questions, ensuring the right response or escalation to an agent.
2. Conversational Voice Interfaces
Voice assistants powered by NLU can handle spoken queries, convert them into actionable instructions, and respond naturally. This is critical for high-volume environments like eCommerce or BFSI call centers.
Example: An eCommerce shopper saying, “I want to return my last order” triggers the NLU system to initiate the return process, check policies, and provide status updates—all automatically.
3. Sentiment and Emotion Analysis
NLU can detect customer emotions, enabling systems to respond empathetically and prioritize urgent issues. This improves satisfaction and reduces churn.
Example: If a healthcare patient texts, “I am frustrated that my lab results are delayed,” NLU recognizes the negative sentiment and escalates the query for faster resolution.
4. Personalized Recommendations
By understanding user preferences and intent, NLU can drive personalization in product suggestions, content, or services.
Example: In SaaS, if a client asks, “Show me reports for last quarter,” NLU identifies the request and provides relevant analytics, enhancing the customer experience.
5. Automation of Routine Tasks
NLU can extract key entities and actions from natural language instructions, automating repetitive tasks like bookings, reminders, or form submissions.
Example: A BFSI platform using NLU can process messages like, “Schedule my EMI payment for Friday,” extracting the date and payment details, then executing the task automatically.
6. Knowledge Management and Insights
NLU helps organizations analyze large volumes of unstructured text—emails, chat logs, feedback—to identify trends, common issues, or improvement opportunities.
Example: A D2C brand can use NLU to analyze customer feedback about a product launch, automatically categorizing comments into themes such as delivery, product quality, or pricing concerns.
Challenges in Natural Language Understanding
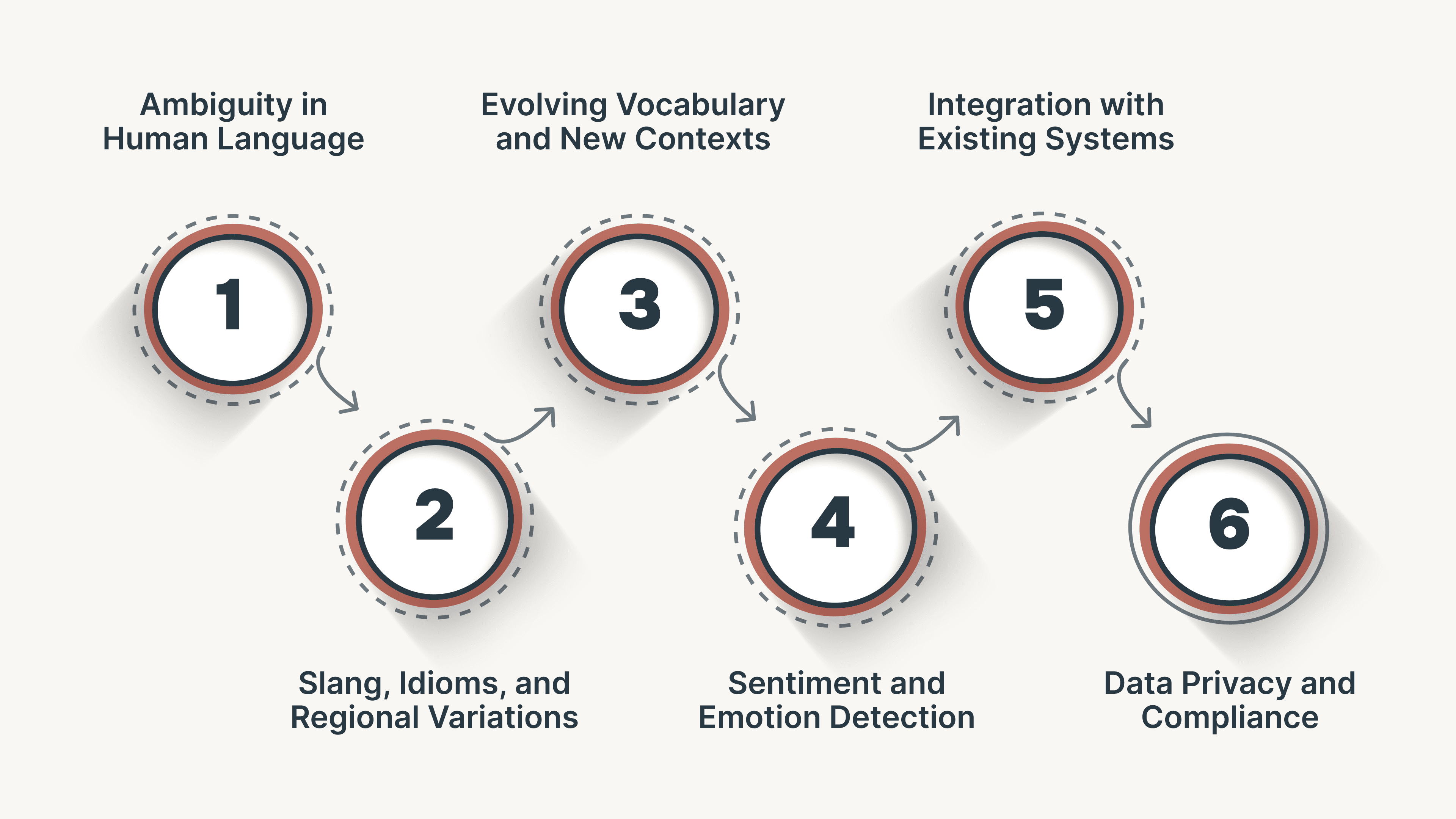
While NLU offers transformative capabilities, implementing it effectively comes with several challenges. Understanding these obstacles helps businesses set realistic expectations and optimize their AI deployments.
1. Ambiguity in Human Language
Human language is often ambiguous, with words and phrases carrying multiple meanings depending on context. For example, a customer saying, “I need help with my account,” could be referring to login issues, billing queries, or updating personal information. NLU systems must accurately interpret intent to avoid incorrect responses.
2. Slang, Idioms, and Regional Variations
In India’s diverse linguistic landscape, customers use slang, regional expressions, and mixed languages. A phrase in Hinglish or a regional dialect can easily confuse an NLU model trained only on standard English, leading to misinterpretation or failure to recognize intent.
3. Evolving Vocabulary and New Contexts
Customer language constantly evolves. New products, services, or trends introduce terms that may not exist in the system’s training data. Without continuous learning, the AI may misclassify or fail to understand these queries, affecting response accuracy.
4. Sentiment and Emotion Detection
Recognizing emotions like frustration, urgency, or sarcasm is challenging. A customer saying, “Great, another delay!” might be sarcastic, but without proper sentiment analysis, the system could misinterpret it as positive feedback, leading to poor customer experience.
5. Integration with Existing Systems
NLU is only effective when it connects seamlessly with CRMs, ticketing systems, or voice platforms. Fragmented data or inconsistent workflows can prevent NLU-powered assistants from delivering accurate, actionable responses.
6. Data Privacy and Compliance
Handling sensitive customer data, especially in BFSI or healthcare, requires strict compliance with regulations like RBI guidelines or HIPAA. NLU systems must anonymize, encrypt, and manage data securely while still delivering an accurate understanding.
Despite these challenges, enterprises can overcome them by using domain-specific models, multilingual capabilities, continuous learning, and integration best practices. When implemented thoughtfully, NLU can deliver consistent, intelligent, and empathetic customer interactions.
Also read: Everything You Need to Know About AI Assistants
Technological Capabilities Required for NLU
Implementing effective NLU requires a combination of core technological capabilities. These are the foundations that allow AI systems to understand human language accurately and act on it in real-time.
Robust Multi-Language Support: NLU systems must handle multiple languages, dialects, and scripts to engage diverse customer bases. Accurate multilingual understanding ensures enterprises across BFSI, e-commerce, and SaaS can provide seamless and inclusive interactions.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Language and user behavior constantly evolve. NLU systems need ongoing training to stay accurate, incorporating new terms, slang, and expressions to maintain relevance and deliver precise responses over time.
Rapid Data Processing and System Integration: NLU relies on fast access to structured and unstructured data. Integration with CRMs, ticketing platforms, and voice systems allows real-time query context, enabling timely and informed responses.
Automation of Actionable Insights: Understanding alone isn’t enough. NLU must convert insights into actions like routing tickets, sending alerts, or escalating issues, ensuring that comprehension leads to tangible operational improvements and better customer experiences.
Together, these capabilities ensure NLU systems not only understand language but also translate it into precise, real-time actions that enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
Transform Customer Engagement with CubeRoot
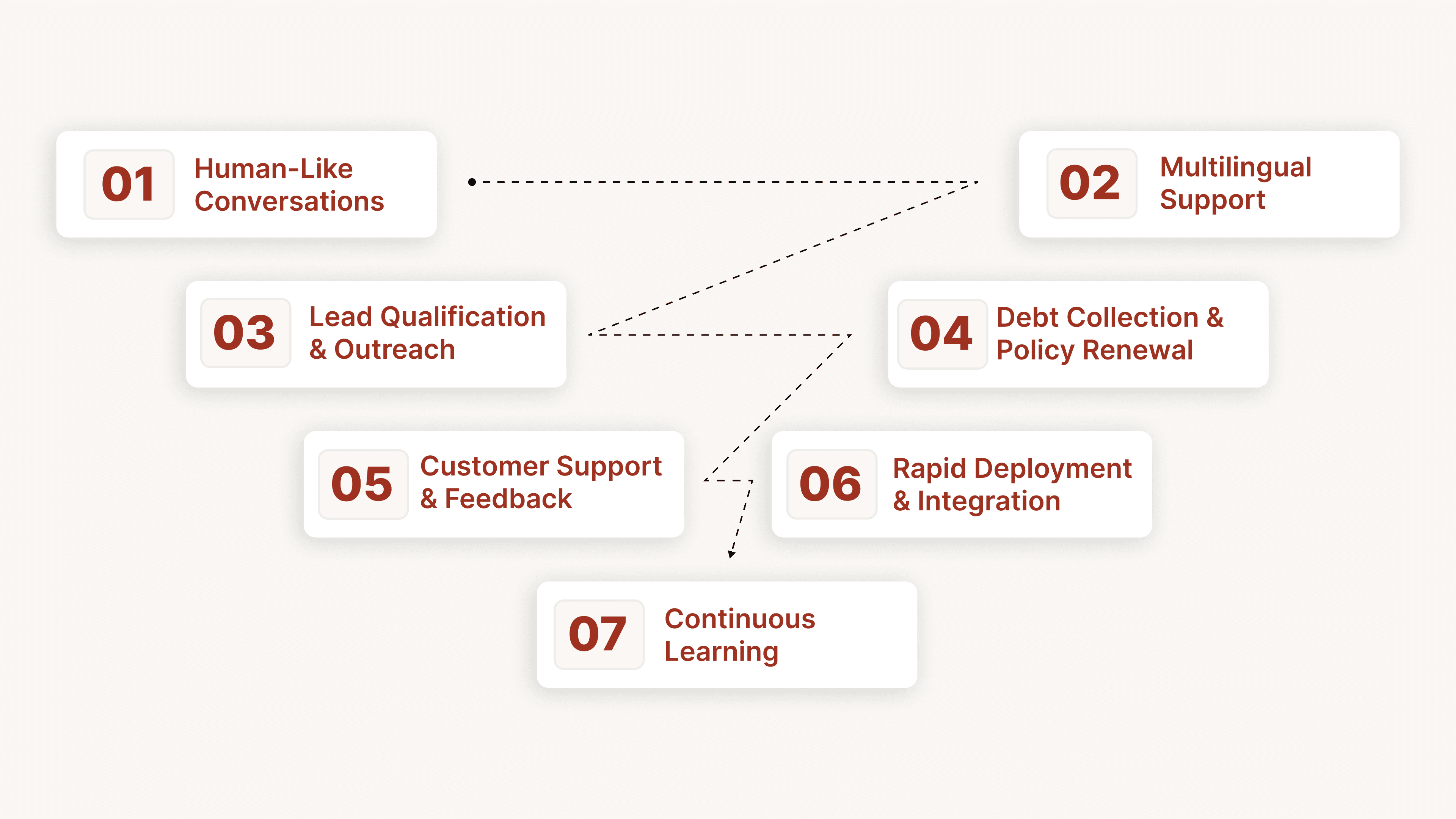
CubeRoot is a Voice AI platform that utilizes Natural Language Understanding to make customer interactions faster, smarter, and more human-like. By understanding intent, context, and sentiment, CubeRoot enables enterprises to deliver seamless, personalized conversations across BFSI, e-commerce, SaaS, D2C, EdTech, and Healthcare.
Here’s how CubeRoot transforms customer engagement:
Human-Like Conversations: CubeRoot’s voice agents speak naturally, detect emotions, and respond dynamically, reducing escalations and improving customer satisfaction.
Multilingual Support: Communicate with customers in English and 11+ Indian languages, making interactions inclusive and accessible.
Lead Qualification & Outreach: Automatically qualify leads and conduct outreach campaigns, enabling teams to reach 3× more prospects without hiring extra reps.
Debt Collection & Policy Renewal: Send personalized reminders, follow-ups, and renewal prompts, boosting recovery rates and reducing costs by up to 50%.
Customer Support & Feedback: Resolve 70% of queries 24/7, capture five times more feedback than traditional surveys, and turn insights into actionable improvements.
Rapid Deployment & Integration: CubeRoot integrates with 150+ CRMs, ticketing systems, and platforms, going live in just 14 days with minimal technical effort.
Continuous Learning: The AI adapts to new phrases, regional slang, and evolving customer behavior, improving accuracy and conversation quality over time.
With the help of NLU, CubeRoot not only understands intent, context, and sentiment but also takes action—resolving queries, capturing feedback, and automating workflows—all in real time.
Ready to transform your customer interactions and drive measurable growth? Request a demo today and see how CubeRoot can work for your business.
FAQs
1. What is an example of Natural Language Understanding (NLU)?
A common example of NLU is a customer support chatbot that can interpret a user query like “I can’t access my account” and distinguish it from a password reset request. The system identifies the intent (login issue) and entities (account details) and routes the request to the correct solution, all without human intervention.
2. Can NLU understand different languages?
Yes. Advanced NLU systems support multiple languages, dialects, and scripts. Multilingual NLU enables businesses to serve diverse customer bases, ensuring accurate understanding and responses regardless of the language used in queries.
3. Is ChatGPT an LLM or NLP?
ChatGPT is a Large Language Model (LLM) built using NLP techniques. NLP provides the underlying methods for processing and understanding language, while the LLM architecture allows ChatGPT to generate human-like text, understand context, and perform tasks such as summarization, translation, and conversation.
4. What is the primary focus of Natural Language Understanding (NLU)?
The primary focus of NLU is to enable machines to understand the meaning, context, and intent behind human language. This allows AI systems to interpret nuances, detect sentiment, and respond appropriately, making interactions with machines more natural and effective.
5. How does NLU differ from NLP?
While NLP covers the overall processing of language, like breaking sentences into words, identifying parts of speech, or analyzing grammar, NLU goes a step further. It focuses on understanding what the words actually mean, the intent behind them, and the context of the conversation. In short, NLP helps machines read language, while NLU helps them truly understand it and respond intelligently.























