Dec 8, 2025
AI-Driven Voice Interaction: A Practical Guide for Indian Enterprises
You know that moment when your call-center logs flood with “I can’t hear you” or “I didn’t get that,” and your team is scrambling to respond with speed, accuracy, and empathy? For enterprises, this isn’t just frustrating; it’s a silent cost drain, a brand perception issue, and a roadblock to their roadmap.
According to recent industry data, fewer than 10% of agent interactions are expected to be fully automated by 2026. That stat sets the stage for why AI-driven voice interaction is no longer optional; it’s becoming essential.
In this guide, you’ll gain a clear understanding of what voice-AI really is, how it works, and where the real value lies. You’ll also learn what traps to avoid and how to navigate this terrain using practical, enterprise-ready frameworks.
Key Takeaways:
Why it matters: Voice-AI is becoming essential for Indian enterprises as rising call volumes and low automation levels make traditional support models unsustainable.
How it works: AI-driven voice interaction relies on ASR, NLU, orchestration, TTS, and deep integrations working together to deliver natural, reliable conversations.
Where value lies: The strongest business impact comes from automating high-volume workflows such as customer support, KYC, field operations, bookings, and lead qualification.
How to deploy: Enterprises see the best results when they follow a structured rollout, moving from PoC to pilot to production with clear KPIs at each stage.
What builds trust: Users stay engaged when the system offers clear prompts, maintains context, supports multilingual inputs, responds quickly, and adheres to strong security practices.
Why CubeRoot helps: CubeRoot unifies calling, data, AI, workflows, and compliance into a single platform designed specifically for Indian enterprises to scale and speed.
What Is AI-Driven Voice Interaction?
At its core, AI-driven voice interaction is technology that allows people to interact with a system in the same way they interact with a human. It listens to your voice, understands what you mean, decides what to do next, and responds back in natural speech. This is done using four building blocks:
ASR (converts speech to text),
NLU (understands intent),
Dialogue logic/LLM (figures out the next action),
TTS (speaks the answer back).
Instead of “Press 1 for billing,” users can simply say “I want my invoice.” The system understands their request and completes the task instantly.
How Enterprises Actually Use It
A customer says, “Track my order.”
The system hears the sentence (ASR).
It understands the intent (NLU).
It fetches the order details from the backend.
It responds, “Your order is arriving tomorrow.”
Also Read: What Is A Voice Chatbot: A Complete Guide
If the “what” explains the experience, the “how” explains the reliability. Voice-AI succeeds only when its underlying components work flawlessly together.
Core Components of AI-Driven Voice Interaction
Enterprises often see voice-AI as “one system,” but under the hood, it’s a coordinated stack of specialized components, each solving a different real-world problem. Understanding these parts is essential before evaluating accuracy, latency, compliance, or scalability.
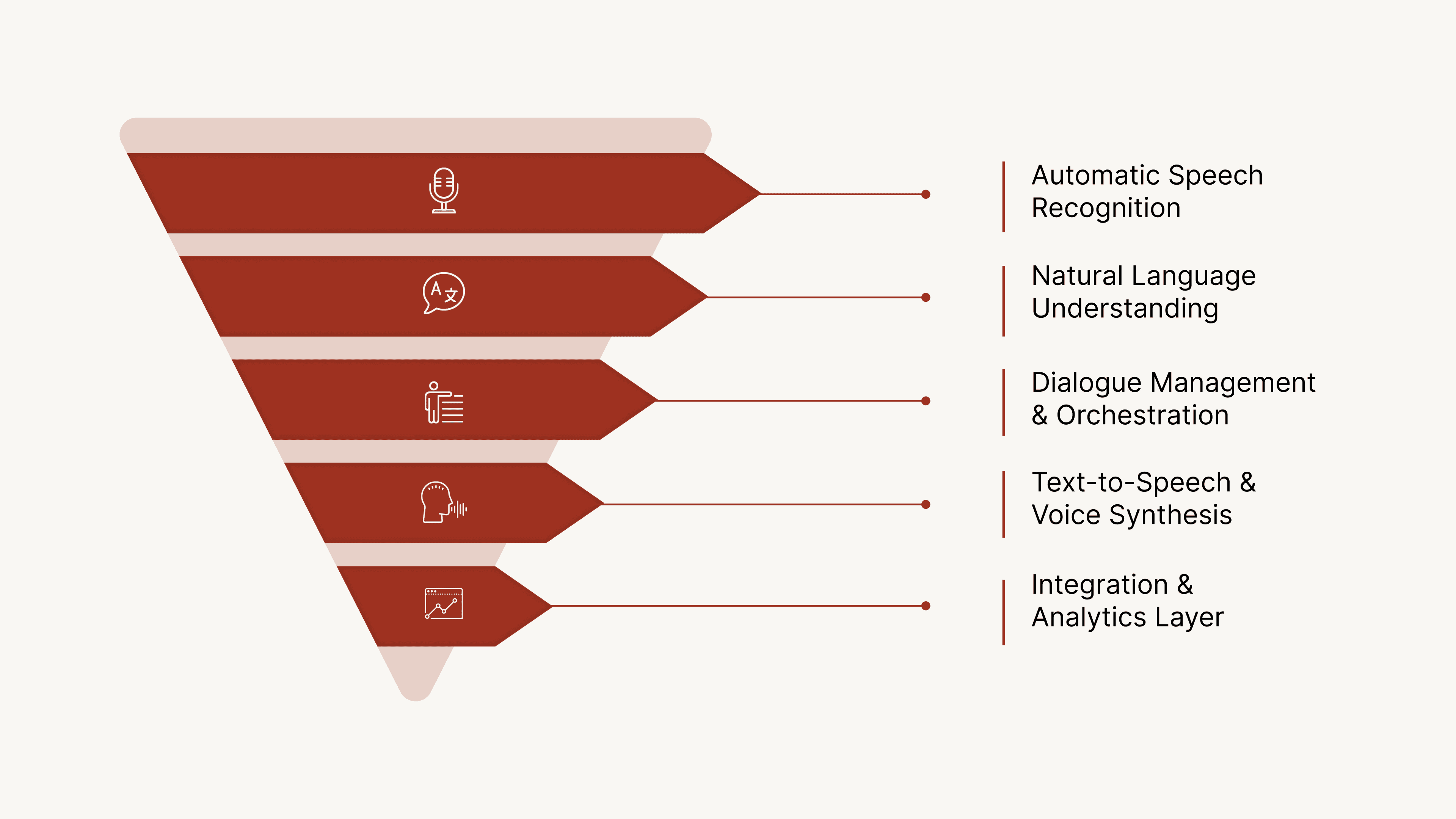
Below is a clear breakdown of the components that actually drive enterprise-grade voice interactions.
1. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
ASR converts live speech into machine-readable text, forming the foundation of every voice interaction. It needs to capture accents, pace, domain vocabulary, and background noise typical of support centers and field conditions.
How it works in an enterprise:
Captures customer speech from phone lines, IVR, apps, or kiosks
Transcribes with high accuracy even when users speak fast, switch languages, or mention technical terms
Supports compliance logging by generating text transcripts
Feeds the transcript to your NLU engine or LLM in milliseconds
2. Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
NLU interprets the meaning behind the customer’s words. Instead of matching keywords, it understands intent, emotion, and context — essential for reducing escalations and repetitive agent hand-offs.
How it works in an enterprise:
Identifies the actual request (“refund,” “card blocked,” “service outage”)
Extracts critical details like order number, location, or date
Understands follow-up questions without restarting the conversation
Routes correctly to workflows or APIs to prevent misclassification
3. Dialogue Management & Orchestration (with LLMs)
This is the decision-making engine. It manages the conversation, decides the next step, triggers backend actions, or escalates to a human when needed. Think of it as the system's operational “control tower.”
How it works in an enterprise:
Maintains conversation history across multiple turns
Chooses the right workflow (refund → verification → status update)
Uses LLM reasoning for open-ended or complex user inputs
Calls enterprise APIs (CRM, ERP, ticketing) to complete real tasks
Applies guardrails for compliance-sensitive steps
4. Text-to-Speech (TTS) & Voice Synthesis
TTS converts system outputs into natural speech. Enterprises rely on this to create consistent, clear, branded voice responses across every customer segment and channel.
How it works in an enterprise:
Delivers lifelike speech that matches your brand’s tone
Adapts pace, emphasis, and clarity for effortless comprehension
Supports multiple languages for diverse user bases
Reduces cognitive load by delivering instructions conversationally
5. Integration & Analytics Layer
This layer connects voice AI to your enterprise systems and measures performance. Without it, voice AI can’t complete tasks or prove ROI.
How it works in an enterprise:
Pulls data from CRMs, ERPs, order systems, or knowledge bases
Pushes updates automatically (raise ticket, update status, log complaint)
Tracks critical metrics like WER, latency, first-contact resolution, and containment
Provides dashboards for quality, compliance, and model improvement
Supports audit trails and governance for regulated industries
Once you understand how these components work together, the practical value becomes easier to see. Voice-AI unlocks several high-impact use cases that Indian enterprises can deploy immediately.
Business Use Cases for Indian Enterprises
For Indian enterprises, the value of voice-AI becomes real only when it solves high-volume, high-friction workflows. Most organizations already deal with long call queues, multilingual customer bases, compliance-heavy processes, and distributed operations.
Here are some high-impact use cases to understand the same.
Automated Customer Support: Handle high-volume queries like order tracking, refunds, billing, and account info without human agents.
Intelligent Call Routing: Replace “Press 1 / Press 2” with natural, intent-based routing for faster resolution.
KYC & Compliance Automation: Capture user details, run verification steps, and log consent for regulated sectors.
Order & Field Operations: Let delivery agents or technicians update status, log reports, or fetch documents using voice.
Appointment & Booking Management: Book, cancel, and reschedule appointments through conversational interfaces.
Internal IT/HR Helpdesk: Answer employee questions on policies, access, password resets, and troubleshooting.
Lead Capture & Qualification: Collect inbound leads, ask qualification questions, and push data into CRM.
Identifying the right use cases is only half the job. The real impact comes from how well the organization rolls out voice-AI across teams, systems, and workflows.
Implementation Roadmap for Indian Enterprises
Deploying voice-AI is not about switching on a bot; it’s a structured operational rollout that touches data, people, compliance, and backend systems. Indian enterprises, especially in BFSI, telecom, retail, healthcare, and logistics, require a roadmap that balances speed with governance.
Here’s the practical path most successful organizations follow:
Implementation Roadmap for Indian Enterprises
Voice-AI succeeds when business intent, data readiness, engineering, and governance are all coordinated.
Below is a phased roadmap that you can follow. Each phase outlines what to do, who is responsible, measurable deliverables, a realistic timeline, and common risks with their corresponding mitigations.
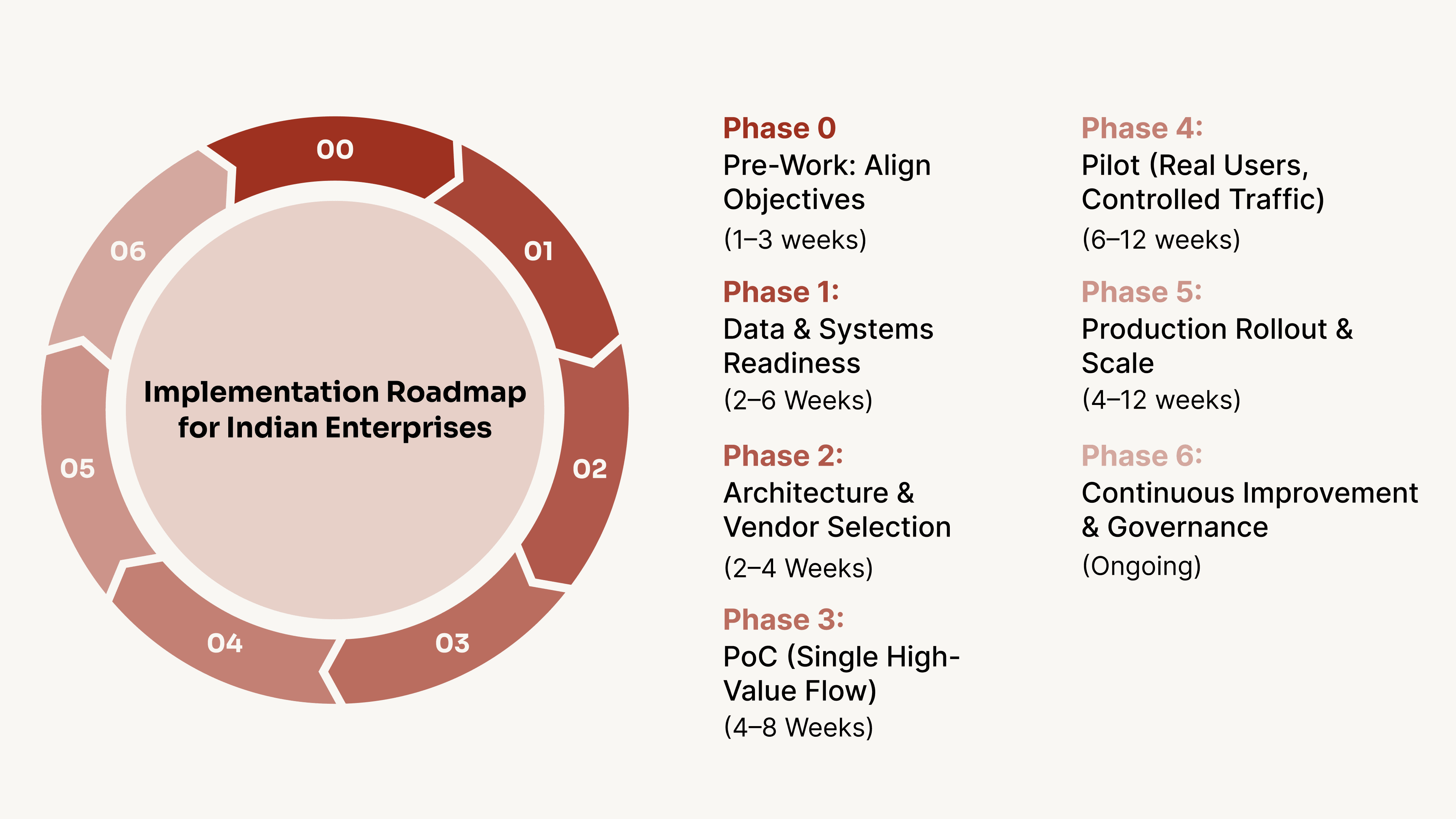
Phase 0: Pre-Work: Align Objectives & Create the Business Case (1–3 weeks)
Before touching any tech, clarify why you’re doing this.
Choose one or two high-value use cases
Set target metrics like containment, AHT reduction, or CSAT lift
Align Product, CX, Tech, Compliance, and Finance
This prevents the common trap of “cool pilot, no production impact.”
Phase 1: Data & Systems Readiness (2–6 Weeks)
Voice-AI is only as strong as the data you feed it.
Review call recordings, transcripts, and knowledge bases.
Check if APIs can actually return the information the voicebot needs.
Ensure PII, consent, and retention policies are in place.
Create a sample set of real customer utterances for training.
This is where most teams underestimate effort, but it sets the foundation
Phase 2: Architecture & Vendor Selection (2–4 Weeks)
Decide whether you need cloud, hybrid, or on-prem, depending on compliance and latency.
Test ASR accuracy on your actual calls.
Test latency on real networks.
Compare the integration effort for your internal systems.
Review SLAs, security, and data residency.
A small technical POC with two or three vendors is extremely valuable here.
Phase 3: PoC (Single High-Value Flow) (4–8 Weeks)
Pick one predictable flow, such as order status, balance enquiry, or appointment scheduling.
Build ASR → NLU → logic → backend API → TTS
Add a human-in-loop review for edge cases.
Measure core metrics like WER, intent accuracy, and basic containment.
A tight PoC proves value faster than a large, unfocused pilot.
Phase 4: Pilot (Real Users, Controlled Traffic) (6–12 weeks)
Expose the system to real customers, but only 10–20% of the traffic.
Track where users drop off.
Analyze why escalations happen.
Monitor latency and failure patterns.
Collect feedback from agents and customers.
This stage reveals multilingual challenges, noisy audio issues, and integration weaknesses before full rollout.
Phase 5: Production Rollout & Scale (4–12 weeks)
Once the pilot stabilises, scale responsibly.
Harden infrastructure and ensure reliability.
Automate model updates and deploy conversation flow.
Add monitoring dashboards, alerting, and incident playbooks.
Expand to new use cases gradually, not all at once.
Think of this as shifting from “project” to “product.”
Phase 6: Continuous Improvement & Governance (Ongoing)
Voice-AI improves with usage.
Use real customer queries to continually improve intent accuracy.
Fix issues shown by drop-offs, escalations, or low-accuracy turns.
Track WER, containment, and latency to maintain performance.
Introduce new tasks only when usage data shows a clear need.
Revalidate consent, retention, and access controls to stay compliant.
Enterprises that treat voice-AI as a living system see compounding gains over time.
With the rollout strategy in place, the next challenge is ensuring the experience feels natural.
Best Practices for Designing Natural Voice Experiences
Users usually decide within the first 10–15 seconds whether the system “gets them,” and this perception shapes trust, drop-offs, and escalation rates. Research from conversational UX studies consistently shows that clarity, predictability, and turn-taking behavior are what make voice systems feel natural.
Here’s how to design voice interactions people actually want to talk to:
Keep prompts short and easy to follow: Avoid long sentences; users respond better to concise guidance.
Give simple suggestions to guide the conversation: Offer examples like “You can say: track my order” to reduce confusion.
Allow users to interrupt naturally (barge-in): People cut in during real conversations; your system should handle it smoothly.
Maintain context across turns: Remember previous questions so users don’t have to repeat themselves.
Use a consistent and appropriate tone: Match the voice style to the task; neutral for support, warm for service.
Handle uncertainty with clarifying questions: Ask for details instead of repeating “I didn’t understand.”
Design for noisy environments: India’s real usage happens in traffic, offices, and shops; keep prompts crisp and ASR tuned.
Support multilingual and mixed-language inputs: Users switch between English and regional languages mid-sentence; NLU must handle this.
Keep response times under 1–1.5 seconds: Delays break trust; fast responses feel more “human.”
Provide an easy path to a human agent: Smooth escalation improves experience and prevents frustration.
Suggested Read: Everything You Need to Know About AI Assistants
Once the experience feels natural, enterprises must ensure it’s also trustworthy.
Data, Security & Compliance Requirements
Voice-AI doesn’t just process conversations; it handles sensitive customer audio, personal data, and compliance-heavy information. That makes security and governance non-negotiable for any enterprise deployment.
Here are the requirements you must get right before scaling.
According to the 2025 “State of Voice AI” report, enterprises list data privacy compliance and strong security as top requirements when deploying voice AI agents.
A security analysis shows that voice-AI systems must move beyond traditional text-based security. For example, one form of attack known as voice prompt injection is now recognized as a major threat vector unique to voice systems.
Enterprise deployments increasingly demand end-to-end encryption, secure data storage, real-time monitoring, and audit trails for voice streams, to meet regulated-industry standards.,
In India, data residency is becoming critical: one provider launched a voice-AI model with India-hosted infrastructure so enterprise voice data remains stored in-country and compliant with local regulations.
Regulatory compliance is cited by 56% of enterprises as a primary reason for adopting voice AI. This indicates that security and governance drive adoption, not just cost or efficiency.
Voice AI market research emphasizes that “voice data is inherently sensitive, raising privacy, consent management and biometric security concerns”. Organizations must adopt comprehensive frameworks.
For voice-AI in regulated sectors (finance, healthcare), real-time compliance monitoring is now built in, with automated flagging of breaches (e.g., PCI-DSS, MiFID II) during live calls.
When security, data residency, and compliance sit at the center of your voice-AI strategy, you need a platform built to meet those realities, not workaround them. CubeRoot offers enterprise-grade governance, auditability, and India-ready infrastructure so your voice automation scales safely and reliably.
Once your data and security foundations are in place, the next step is proving that the system is actually working. That’s where tracking the right KPIs becomes essential.
KPIs & Success Metrics for Voice Interaction
Track metrics that tie tech performance to business outcomes. These KPIs show whether your voice AI is accurate, fast, cost-effective, and actually reducing human load.
KPI | What it Indicates | Good Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
WER (Word Error Rate) | ASR accuracy | < 10–15% in clean audio |
End-to-End Latency | Speed of response | < 1–1.5 sec per turn |
Containment Rate | How many queries does the bot resolve without agents | 50–75% |
Intent Accuracy | Correct understanding of user requests | 85–90%+ |
Escalation Rate | % of calls handed to humans | < 15–25% |
AHT Impact | Reduction in handling time | 20–50% improvement |
CSAT | User satisfaction | Should match or exceed agent-handled CSAT |
Cost-to-Serve | Cost per automated interaction | Should trend down as containment rises |
Also Read: Automated Calling System for Businesses
Strong KPIs highlight opportunities, but they also expose weaknesses. To scale voice-AI confidently, enterprises need to anticipate these challenges and address them proactively.
Key Challenges & How to Overcome Them
While the tech may work in controlled tests, real-world deployment brings new obstacles, spelling the difference between transformative ROI and abandoned projects.
Below are major challenges with practical strategies to handle them.
Challenge | Why it happens | How to fix it |
|---|---|---|
High latency | Users drop off when responses take >1 sec (research shows satisfaction drops sharply beyond 500ms). | Use streaming ASR/TTS, optimise APIs, deploy closer data centers/edge. |
Weak integrations | Most failures come from CRM/ERP/API gaps. | Start with one flow, map APIs early, and choose vendors with ready connectors. |
Poor data quality | Limited accents, noise, and domain terms reduce accuracy. | Collect diverse utterances, include noisy samples, and refresh data often. |
User mistrust after errors | One misunderstanding can lower reuse rates. | Add clear fallbacks, allow human escalation, and use clarifying prompts. |
Security & spoofing risks | Voice systems face deepfake and injection attacks. | Apply MFA, spoof detection, encryption, and strict access controls. |
Unclear ROI | Hard to justify spending without measurable gains. | Track KPIs (containment, latency, AHT), review impact monthly. |
Solving these hurdles requires a platform built for scale, compliance, and Indian enterprise realities. CubeRoot is designed exactly for that.
How CubeRoot Helps Indian Enterprises Build Voice AI
Most enterprises don’t fail at voice-AI because of poor tools — they fail because everything operates in silos. Telephony, CRM, workflows, prompts, and compliance live on different islands, slowing down automation and capping accuracy before it ever reaches scale.
CubeRoot solves this by bringing all of it into one unified platform built for Indian enterprise realities. Teams see 2× faster deployments, 80% quicker lead qualification, and 25–40% higher CSAT because calling, data, AI, and workflows finally work together instead of against each other.
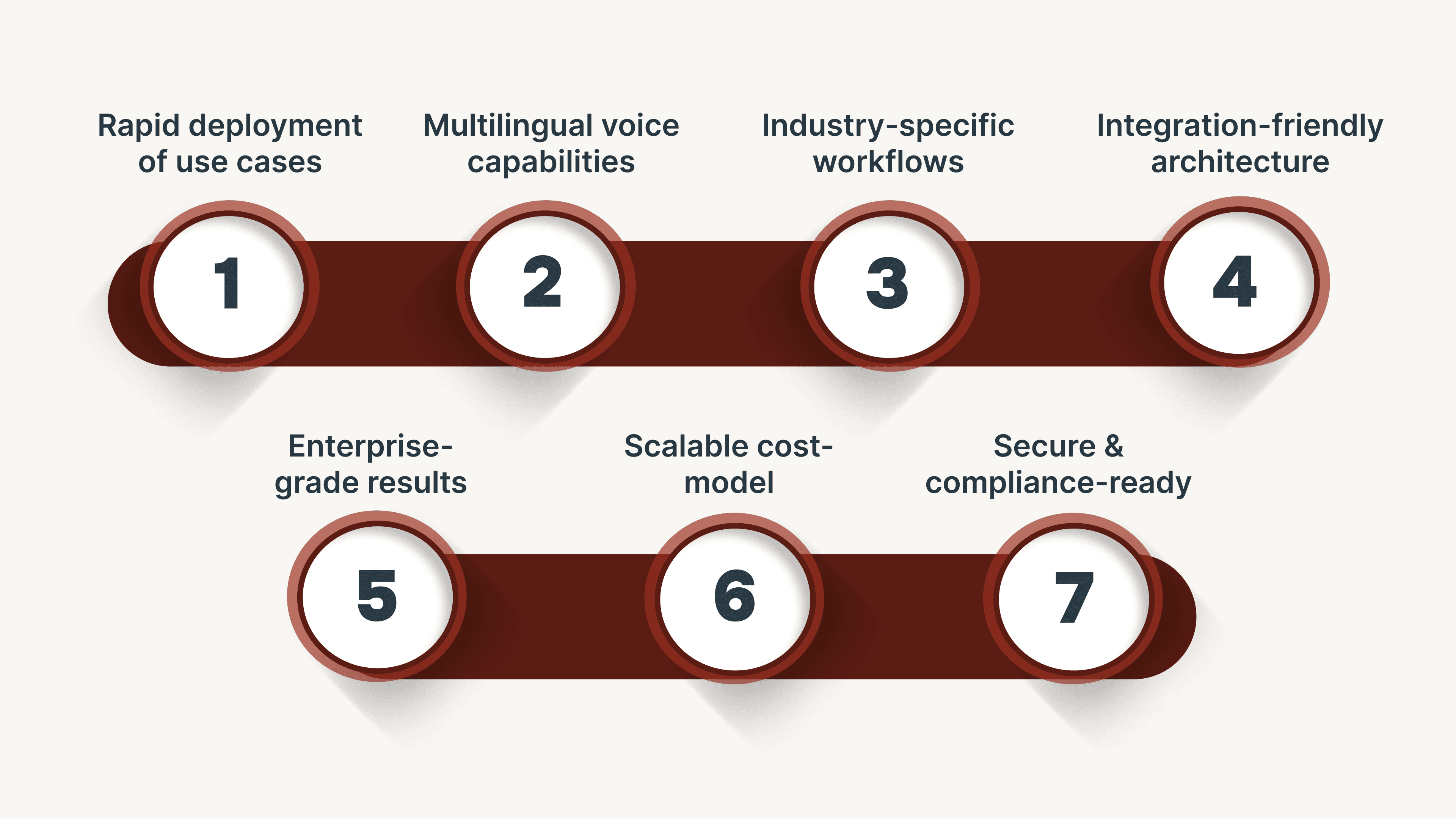
These capabilities show why CubeRoot fits real-world enterprise needs:
Rapid deployment of use cases: Templates and a GenAI prompt builder allow enterprises to go live in days instead of months.
Multilingual voice capabilities: Agents support Hindi + English and Indian regional languages, plus mixed-language speech, reducing friction for Indian customers.
Industry-specific workflows: Ready-made flows for lead qualification, debt-collection, ticketing, service automation in verticals like NBFCs and Real Estate.
Integration-friendly architecture: 50+ out-of-the-box connectors to CRM, telephony, and ticketing systems accelerate deployment.
Enterprise-grade results: Claims such as 90% automation of inquiries, 40% CSAT uplift, or 35% reduction in overdue accounts demonstrate business impact.
Scalable cost-model: Designed for high-volume voice interactions at a fraction of human-agent cost (“1/10th the cost”).
Secure & compliance-ready: Built with audit trails, data governance, and Indian enterprise deployment in mind.
To understand how CubeRoot can fit into your workflows, schedule a demo and walk through the platform with our team.
FAQs
1. How is voice-AI different from the IVR systems we already use?
Voice-AI understands natural speech, intent, and context. Unlike IVRs, which rely on fixed menus. It can handle open queries, such as “I need to update my KYC,” not just “Press 1 for X.”
2. How accurate is AI-driven voice interaction in real business environments?
Accuracy depends on ASR + NLU quality, but well-tuned systems achieve strong intent accuracy even with mixed languages, accents, and noisy conditions.
3. How long does it take to deploy a production-ready voicebot?
POCs take 4–8 weeks, pilots take 6–12 weeks, and full-scale rollouts generally take 3–6 months depending on integrations. CubeRoot claims deployment in as fast as 14 days for templated flows.
4. What does an enterprise need in place before implementing voice-AI?
You need clean data sources, accessible APIs, consent/PII policies, and a clear list of tasks you want to automate.
5. What risks or challenges should enterprises be prepared for with voice-AI?
Common challenges include latency issues, integration gaps, poor data quality, user trust, and compliance requirements; all of which require early planning.























