Dec 29, 2025
Agentic AI Voice Agents: Future-Ready Customer Engagement 2026
For years, enterprise automation has relied on rule-based chatbots and IVR systems that follow scripts rather than conversations. They save time, but only when customers speak the system’s language. The result is often rigid interactions that stall before reaching a resolution.
That’s changing fast. A new generation of agentic AI voice agents is emerging, intelligent systems that don’t just respond but understand, reason, and act. They recognize intent, adjust tone, retrieve information from enterprise systems, and complete multi-step goals without human intervention. Agentic AI market hit $5.99B in 2024 and is set to surge from $7.29B in 2025 to $88.35B by 2032 at 42.8% CAGR.
In this blog, we’ll explore what makes these agents “agentic,” how they differ from conventional automation, and why they’re becoming a strategic priority for enterprises aiming to deliver consistent, human-like service at scale.
Key Takeaways
Agentic AI voice agents go beyond scripted automation by reasoning, planning, and acting autonomously.
They manage real workflows such as payments, lead qualification, and service follow-ups across sectors.
Context retention, multilingual fluency, and adaptive learning make them far more capable than traditional bots.
Enterprises can deploy them quickly through API-based integration, compliance-ready data handling, and human oversight.
2026 marks the turning point where agentic voice automation becomes a core enterprise capability, not a pilot experiment.
What Is “Agentic AI”? Understanding the Core Concept
Agentic AI refers to systems that operate with autonomy, awareness, and goal orientation. Unlike traditional automation, which reacts to commands, an agentic system can plan actions, make contextual decisions, and execute tasks across multiple steps to achieve defined outcomes.
In simpler terms, agentic AI doesn’t wait for instructions; it pursues objectives. It understands why something needs to be done, not just what to do next.
Agentic AI combines reasoning, planning, memory, and adaptability into a unified architecture. This makes it the backbone of the next generation of voice agents capable of handling real-world enterprise operations without constant human supervision.
Now that the foundation is clear, the next step is understanding what specifically makes an AI voice agent “agentic” in practice.
What Makes an AI Voice Agent “Agentic”? Key Capabilities
Agentic AI voice agents go far beyond scripted dialogue. They bring together cognition, context, and control to handle real-world workflows with autonomy and accuracy.
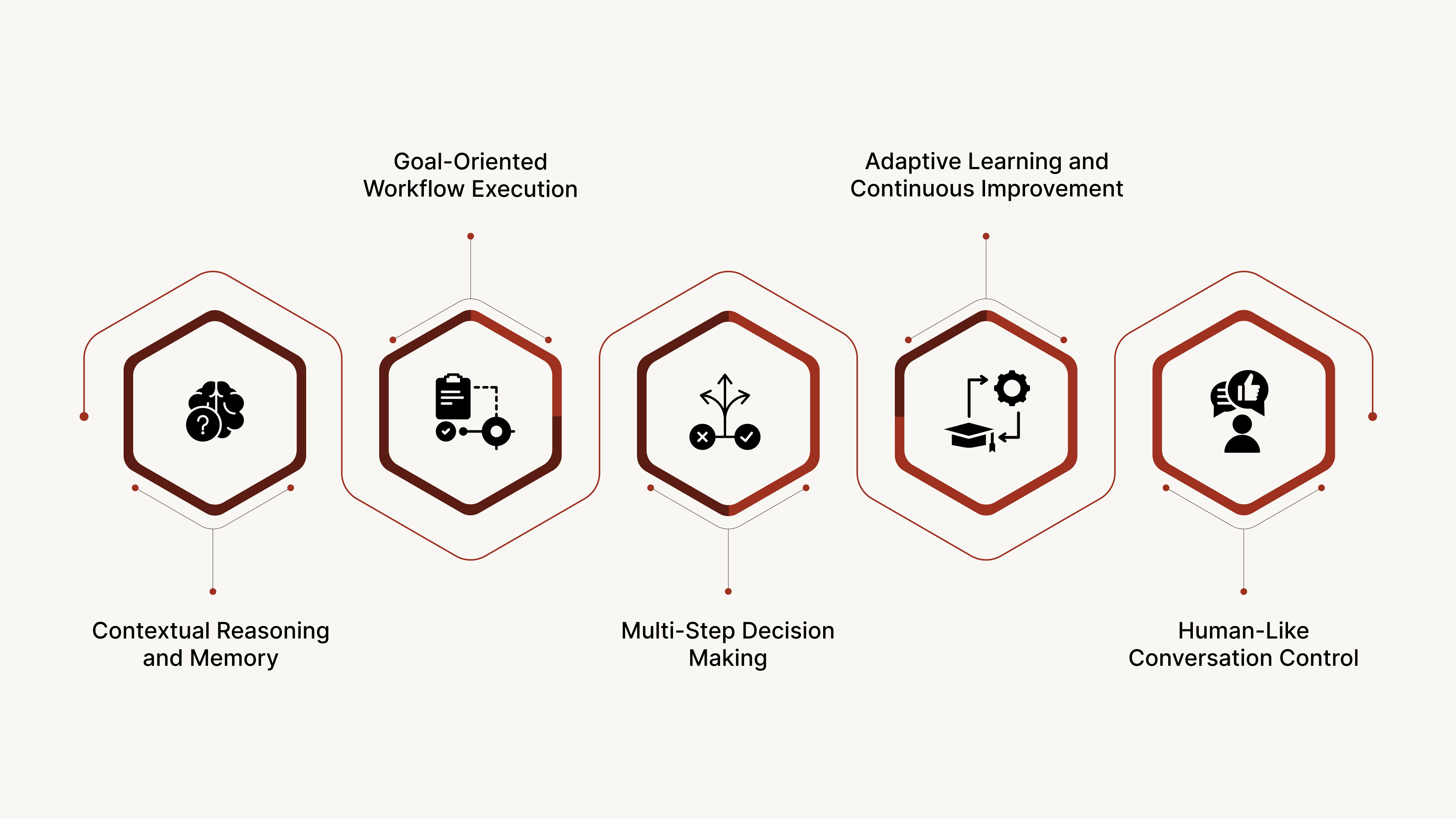
1. Contextual Reasoning and Memory
They retain context across entire conversations instead of treating each interaction as new.
Example: A customer who calls about a delayed delivery later receives proactive follow-ups on resolution status without restarting the discussion.
2. Goal-Oriented Workflow Execution
Agentic voice agents pursue defined objectives instead of offering isolated responses.
Example: For a loan collection process, the agent verifies details, reminds the customer, confirms commitment to pay, and logs it in the system.
3. Multi-Step Decision Making
They plan and adapt through several steps, switching between dialogue, backend actions, and external systems as needed.
Example: If a customer requests rescheduling, the agent checks available slots, updates the CRM, and confirms the change within the same call.
4. Adaptive Learning and Continuous Improvement
Reinforcement learning and feedback loops help them improve response accuracy and language understanding over time.
Example: When customers use new expressions, the model gradually adapts to interpret them correctly.
5. Human-Like Conversation Control
They adjust tone, pacing, and recognition patterns to match natural speech, ensuring clear and empathetic exchanges across languages.
These capabilities make agentic AI voice agents more than automated responders. They function as intelligent digital collaborators capable of managing complete operational loops.
The contrast becomes sharper when we compare them directly with traditional chatbots and rule-based voice systems.
Related: Everything You Need to Know About AI Assistants
Where Agentic AI Voice Agents Outperform Traditional Voice and Chatbots
Traditional voice bots and chat systems were built to follow scripts. They could handle predictable inputs but often broke down when users deviated or when context extended across multiple steps. Agentic AI voice agents are built to handle those exact limitations by reasoning, planning, and executing actions across systems.
Traditional Voice Bot / Chatbot | Agentic AI Voice Agent |
Reacts only to direct prompts | Understands intent and acts proactively based on context |
Operates within rigid scripts | Adapts to new situations and incomplete inputs |
Handles one question or task at a time | Manages end-to-end workflows with multiple steps |
Depends on predefined responses | Generates contextually relevant answers dynamically |
Minimal integration with backend tools | Connects to CRMs, ERPs, and APIs to execute real actions |
Offers limited personalization | Learns from prior interactions to tailor future responses |
Requires human intervention for complex cases | Handles most scenarios independently, escalating only when necessary |
The difference lies in purpose. Traditional bots focus on containment, while agentic voice agents focus on completion. They are not designed to reduce human effort alone but to deliver outcomes that feel human in quality and enterprise-grade in reliability.
To see their real value, it helps to explore where enterprises are already applying agentic voice agents for measurable impact.
Strategic Use Cases for Enterprises
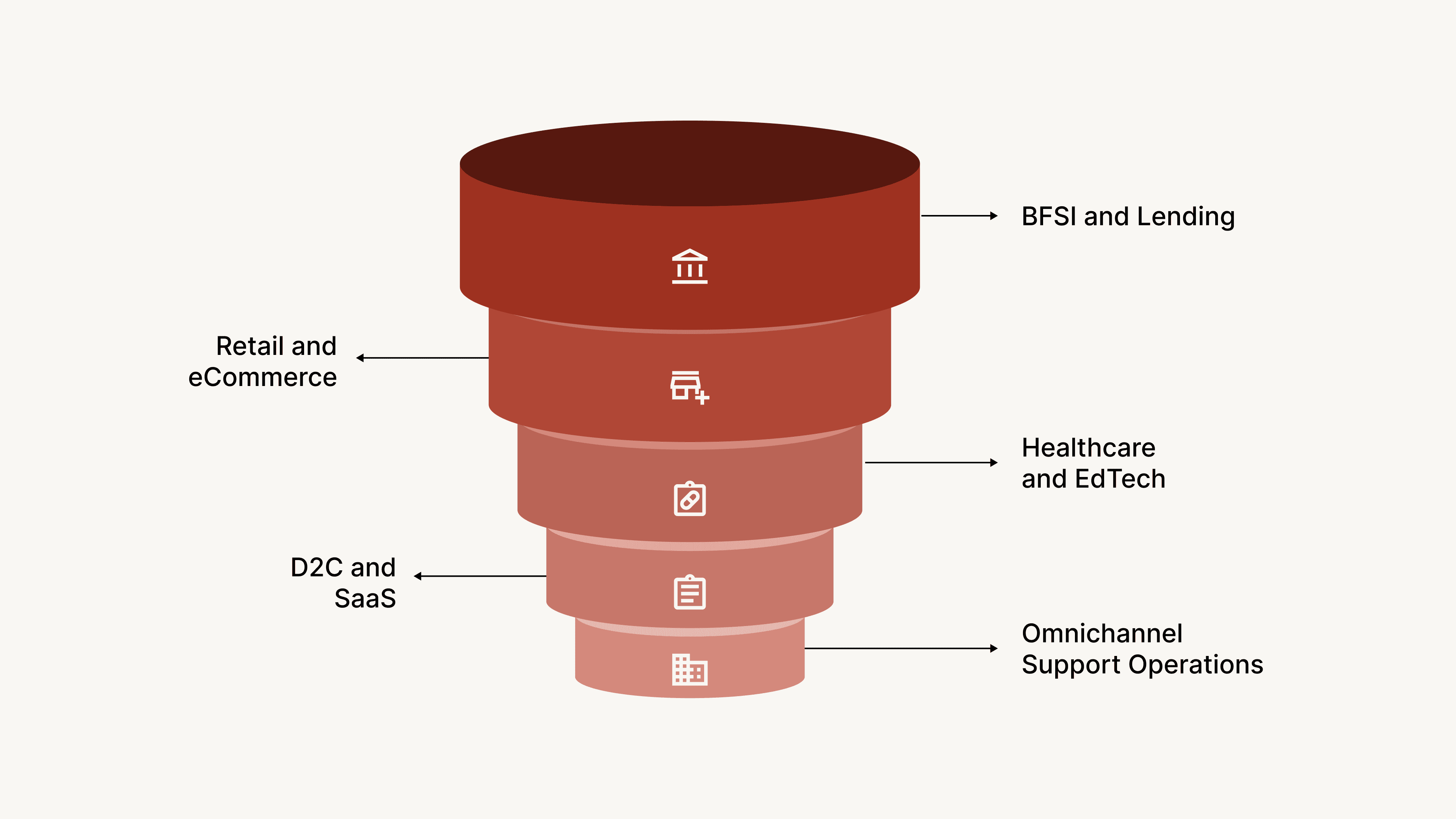
Agentic AI voice agents are built for real business operations, not just customer greetings or FAQs. They perform outcome-driven tasks that previously required entire support or operations teams. Here are the sectors where they deliver the highest impact.
1. BFSI and Lending
Automate payment reminders, loan status updates, and policy renewals.
Confirm customer identity, record consent, and log all interactions for compliance.
Reduce agent dependency during cyclical spikes in repayment calls.
Example: A lending firm can run thousands of repayment reminder calls daily with a consistent tone and verified records.
2. Retail and eCommerce
Manage order tracking, delivery confirmations, and return coordination.
Handle post-sale follow-ups and service feedback in multiple languages.
Keep CX quality stable during festive or promotional surges.
Example: A retailer can use voice automation to process large volumes of delivery updates during seasonal peaks without expanding headcount.
3. Healthcare and EdTech
Confirm appointments, reschedule slots, and send pre-visit instructions.
Gather post-service feedback and escalate issues to human staff if needed.
Maintain compliance for sensitive or regulated communications.
Example: A hospital network can automate appointment confirmations and reminders, ensuring fewer no-shows and faster response cycles.
4. D2C and SaaS
Qualify leads, verify intent, and route high-interest customers to sales teams.
Conduct subscription renewals, billing reminders, and feedback collection.
Track engagement data to refine targeting for future campaigns.
Example: A SaaS provider can use voice agents to handle renewals, freeing human teams for consultative sales.
5. Omnichannel Support Operations
Manage inbound and outbound calls with unified context.
Bridge chat, email, and voice workflows into one conversational layer.
Escalate seamlessly to live agents with complete call context when required.
Example: A telecom operator can unify contact center operations so customers receive the same experience whether they call, text, or use an app.
Agentic voice agents transform enterprise communication from reactive support to proactive engagement, closing the loop between conversation and action.
Before deploying these use cases at scale, organizations must ensure their systems and processes are ready for agentic automation.
What It Takes to Deploy Agentic AI Voice Agents
Successful deployment of agentic AI voice agents depends on more than technology. It requires aligned systems, clear governance, and operational readiness to support autonomy at scale.
1. Integrated Backend Systems
Ensure CRMs, ERPs, and order or claims systems can communicate through secure APIs. Agentic voice agents rely on real-time data exchange to complete tasks such as verifying details or updating records.
2. Data Governance and Compliance Structure
Establish voice data handling policies for encryption, consent, and retention. This is crucial for regulated sectors like BFSI and healthcare, where compliance must be auditable.
3. Multilingual Speech Infrastructure
Adopt models trained on regional languages, accents, and mixed-language usage. Accurate recognition and natural speech generation improve accessibility and trust.
4. Feedback and Monitoring Loop
Set up continuous tracking for call outcomes, intent accuracy, and escalation patterns. Use this data to refine prompts, improve routing, and retrain models periodically.
5. Human-in-the-Loop Framework
Define when and how human agents step in. Clear escalation rules ensure that complex or sensitive cases are resolved seamlessly without breaking the customer experience.
6. Security and Hosting Environment
Deploy the platform in secure, India-based cloud environments with ISO or SOC certification to maintain compliance with local data regulations.
7. Change Management and Training
Prepare teams early. Train staff to interpret AI analytics, manage exceptions, and collaborate with automation rather than compete against it.
An enterprise that builds this foundation can adopt agentic AI confidently, balancing innovation with reliability and compliance.
Even with readiness in place, leaders must anticipate challenges and design safeguards that keep automation stable and trustworthy.
Also Read: What is Conversational AI Analytics?
Risks, Misconceptions, and Mitigations
Implementing agentic AI voice agents offers major advantages, but success depends on managing the right expectations and planning for real-world challenges. The most common risks can be mitigated with the right strategy and structure.
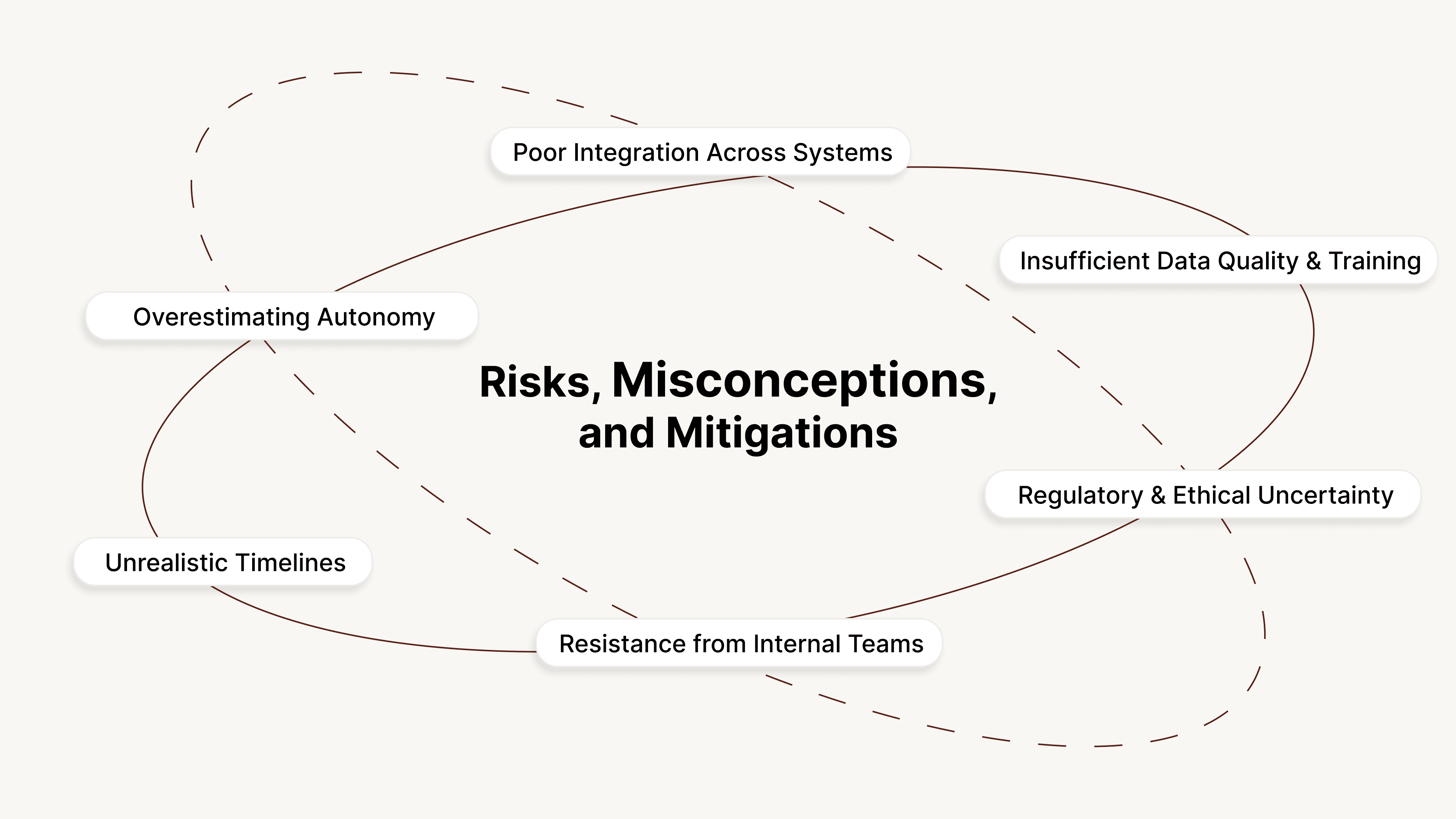
1. Overestimating Autonomy
Risk: Some organizations expect agentic AI to replace human oversight entirely.
Mitigation: Use it to enhance, not eliminate, human participation. Keep humans in the loop for compliance, exceptions, and emotional interactions.
2. Poor Integration Across Systems
Risk: When data sources are fragmented, AI cannot act on real-time information, reducing accuracy.
Mitigation: Standardize APIs and synchronize core systems before launching full-scale deployments.
3. Insufficient Data Quality and Training
Risk: Inaccurate or outdated customer data weakens model learning and response precision.
Mitigation: Clean and maintain enterprise databases, and use reinforcement learning from real calls to improve understanding.
4. Regulatory and Ethical Uncertainty
Risk: Lack of transparency in how AI handles customer data or decisions may create compliance issues.
Mitigation: Use clear disclosures at the start of calls, record and encrypt every interaction, and follow sector-specific audit standards.
5. Resistance from Internal Teams
Risk: Agents and support teams may view automation as a threat rather than a productivity tool.
Mitigation: Involve teams early, communicate its collaborative intent, and track efficiency gains to demonstrate shared value.
6. Unrealistic Timelines
Risk: Expecting overnight results can lead to underprepared rollouts and inconsistent outcomes.
Mitigation: Start small with focused pilots, measure impact, and scale gradually once results are stable.
Agentic AI is most effective when deployed with structure, transparency, and iteration. It thrives in organizations that view automation as a long-term capability, not a quick fix.
With these risks addressed, it’s easier to see why the next few years, particularly 2026, represent a tipping point for enterprise adoption.
Why Enterprises Will Scale Agentic Voice Automation in 2026
Agentic AI voice agents are entering a phase of rapid maturity. Advances in infrastructure, affordability, and AI reasoning are aligning with enterprise priorities, making 2026 the year they shift from pilot to standard practice.
1. Smarter Infrastructure and Speech Models
Improved ASR and NLU models now process multilingual and mixed-language inputs with near-human precision. Low-latency networks and cloud infrastructure make real-time automation feasible even for large-scale voice operations.
2. Growing Demand for Outcome-Based Automation
Enterprises no longer seek chatbots that just deflect tickets. They want systems that close workflows from payment confirmation to appointment scheduling — and deliver measurable business outcomes.
3. Regulatory Push for Verifiable Communication
Financial and healthcare regulators now emphasize consent, auditability, and transparency in customer communication. Agentic voice agents naturally meet these requirements through built-in call logging and transcript-based verification.
4. Customer Behavior Favors Voice
Indian consumers continue to trust voice interactions over text, especially in complex or high-value transactions. Multilingual, context-aware AI agents can bridge this trust with scalability and consistency.
5. Enterprise Focus on Efficiency and CX Convergence
Customer experience, compliance, and cost reduction are now part of the same strategic goal. Agentic automation delivers all three by ensuring faster responses, consistent tone, and controlled operational cost.
These converging trends make 2026 the inflection point where agentic AI voice agents move from innovation labs to enterprise command centers.
With the timing right, the next step is understanding how enterprises can launch effective pilots and scale responsibly.
Also Read: How Voice Assistants Enhance Delivery Updates for Businesses?
How to Get Started with Agentic AI Voice Agents
Deploying agentic AI voice agents successfully starts with structure. Enterprises that follow a phased roadmap minimize risk, accelerate adoption, and measure value effectively.
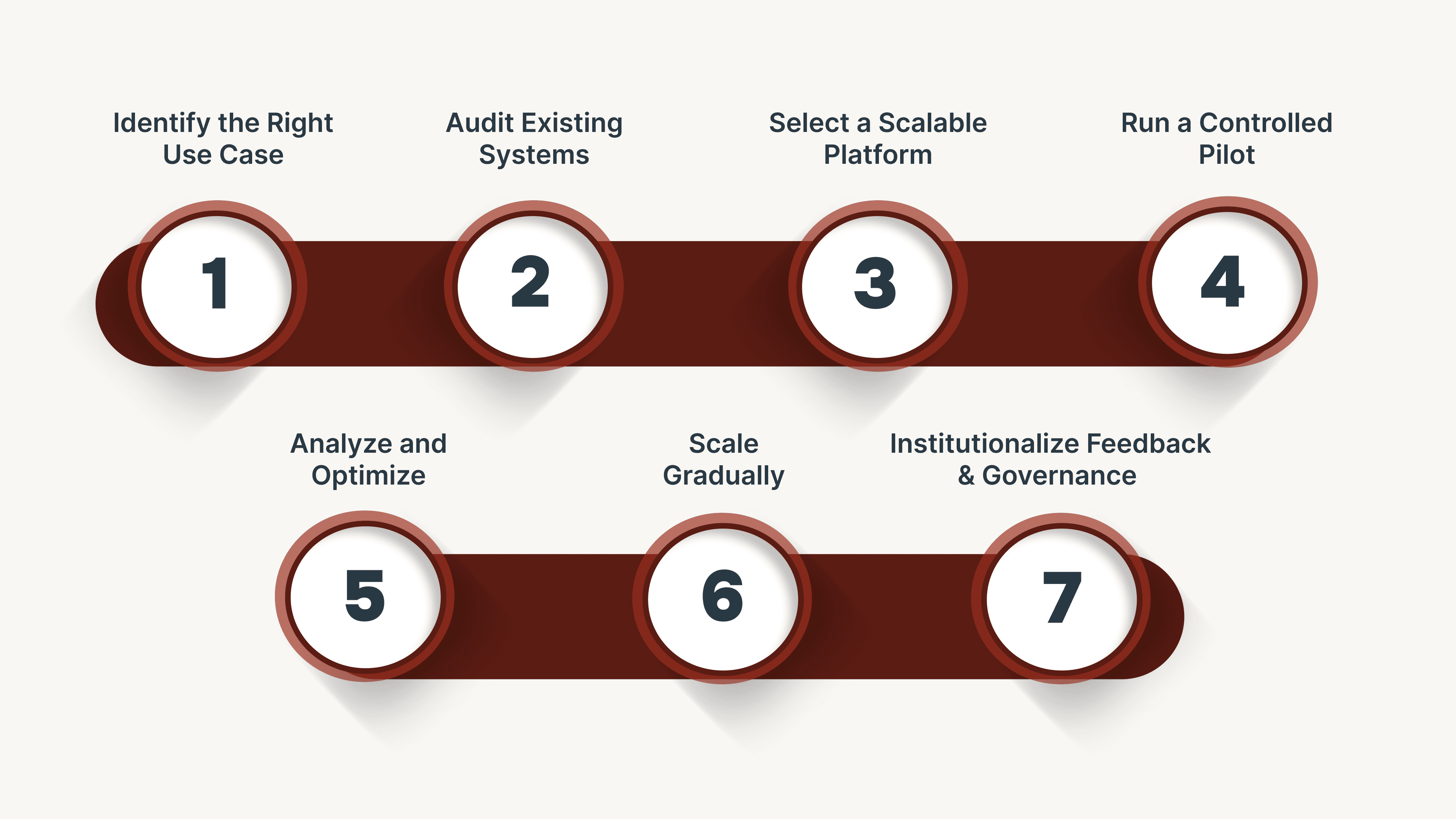
Step 1: Identify the Right Use Case
Choose high-volume, repeatable voice workflows such as payment reminders, order confirmations, or appointment scheduling. Focus on areas where automation can deliver measurable gains in accuracy or response time.
Step 2: Audit Existing Systems
Review CRM, ERP, and telephony systems to ensure they support real-time data access through APIs. Clean and standardize records so the AI can act on reliable information.
Step 3: Select a Scalable Platform
Pick a platform that supports multilingual interaction, secure voice logging, and continuous learning. Look for compliance certifications, quick deployment capabilities, and integration flexibility.
Step 4: Run a Controlled Pilot
Start small with one department or process. Track metrics such as resolution rate, escalation frequency, and sentiment consistency to validate results.
Step 5: Analyze and Optimize
Use pilot data to identify gaps, retrain models, and refine conversation flows. Include human feedback in this loop to balance automation with accuracy.
Step 6: Scale Gradually
Expand to more processes once the AI consistently meets KPIs. Integrate with analytics dashboards and monitoring tools to maintain transparency across departments.
Step 7: Institutionalize Feedback and Governance
Create a long-term framework for ongoing training, compliance review, and performance evaluation. This ensures the system continues learning and improving as business dynamics evolve.
Following these steps transforms agentic AI deployment from an experiment into a sustainable enterprise capability.
Once the roadmap is clear, the final step is to recognize how this technology will continue shaping enterprise communication strategy in the years ahead.
How CubeRoot Accelerates Agentic AI Voice Automation
Turning agentic AI from concept to enterprise reality requires infrastructure that blends intelligence, security, and speed. CubeRoot’s voice platform is purpose-built for high-volume, regulated industries where precision and customer trust matter most.
Pretrained Industry Models: Purpose-built workflows for BFSI, retail, healthcare, and D2C allow fast rollout of agentic voice applications without heavy customization.
Rapid Go-Live: API-first integration and no-code configuration shorten the path from pilot to production to under two weeks.
Human-Like Multilingual Agents: Emotion-aware speech and mixed-language fluency make every interaction sound natural, improving engagement across regional markets.
Continuous Learning: Real-time transcription and feedback systems keep performance improving through data-driven iteration.
Compliance and Data Sovereignty: All voice data is encrypted, logged, and hosted securely within India to meet regulatory and enterprise-grade security requirements.
By combining agentic reasoning with operational scalability, CubeRoot helps enterprises turn automation into a growth advantage where every customer call becomes an intelligent, outcome-driven conversation.
Ready to automate complex workflows, strengthen compliance, and scale customer operations intelligently? Schedule a demo to see agentic voice automation in action.
FAQs
1. What makes an AI voice agent “agentic”?
An agentic AI voice agent can reason, plan, and execute multi-step goals autonomously. Unlike scripted bots, it understands intent, accesses enterprise data, and completes real tasks such as payments, scheduling, or lead qualification.
2. How is agentic AI different from generative AI?
Generative AI focuses on content creation or language generation, while agentic AI focuses on autonomous decision-making and workflow execution. In short, generative AI responds; agentic AI acts.
3. Can agentic AI voice agents handle multilingual and mixed-language calls?
Yes. Modern models are trained on Indian speech patterns, accents, and code-mixed languages like Hinglish and Tamlish, allowing natural conversations across regional audiences.
4. Are agentic voice agents compliant with sector regulations?
When deployed on secure, auditable platforms, they meet compliance requirements across BFSI and healthcare through encrypted data storage, call recording, and transparent consent.
5. How can an enterprise start with agentic voice automation?
Begin with a targeted pilot around a high-volume, repetitive process such as payment reminders or order confirmations. Evaluate impact, refine the flow, and scale gradually across departments.























